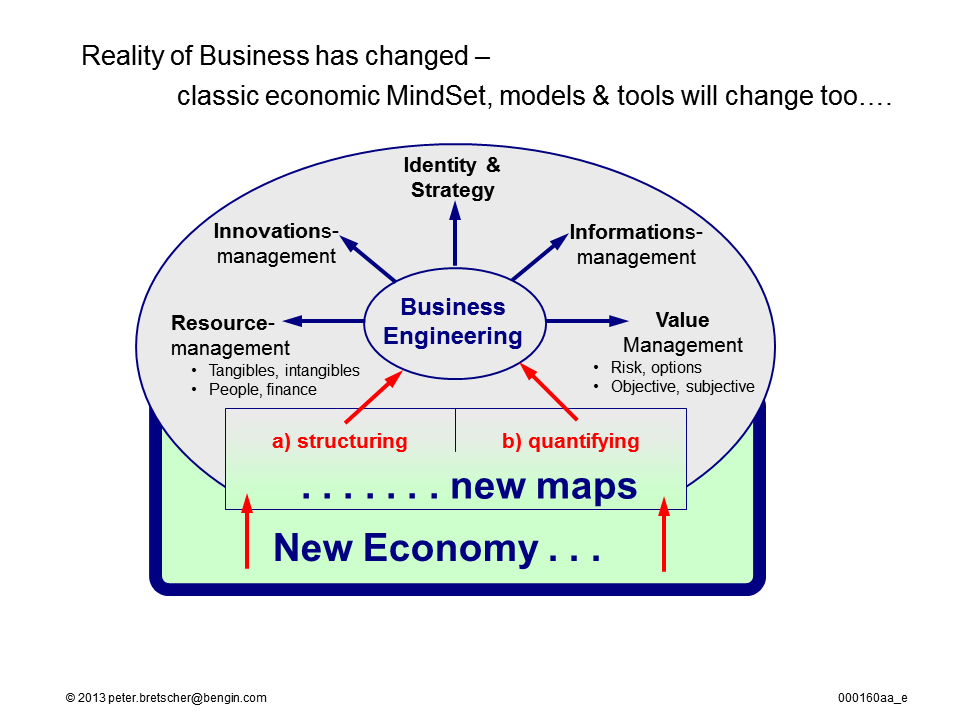
A hybrid metric is a combination of two or more metrics that are used to measure a specific business objective. Hybrid metrics are often used to provide a more holistic view of performance than traditional metrics, which can be too narrow in focus.
For example, a company might use a hybrid metric to measure the effectiveness of its marketing campaigns. This metric could combine data on website traffic, lead generation, and sales to provide a more complete picture of how the campaigns are performing.
Hybrid metrics can be used to track a wide range of business objectives, including customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and financial performance. By using hybrid metrics, businesses can get a better understanding of how their various initiatives are impacting their overall performance.
Here are some of the benefits of using hybrid metrics:
They provide a more holistic view of performance. Traditional metrics can be too narrow in focus and can miss important insights into how a business is performing. Hybrid metrics can provide a more complete picture by combining data from multiple sources.
They can help to identify areas for improvement. By tracking multiple metrics, businesses can identify areas where they are performing well and areas where they need to improve. This information can be used to make strategic decisions about how to allocate resources and improve performance.
They can help to improve communication with stakeholders. By using hybrid metrics, businesses can communicate their performance in a more comprehensive and persuasive way to stakeholders, such as investors, customers, and employees.
If you are looking for a way to get a better understanding of your business performance, hybrid metrics can be a valuable tool. By combining data from multiple sources, hybrid metrics can provide a more holistic view of performance and help you to identify areas for improvement.
Here are some examples of hybrid metrics:
Customer satisfaction score: This metric combines data on customer surveys, social media engagement, and customer churn to measure how satisfied customers are with a company’s products or services.
Employee engagement score: This metric combines data on employee surveys, attendance, and turnover to measure how engaged employees are with their work.
Financial performance: This metric combines data on revenue, expenses, and profit to measure the financial performance of a company.
Improve decision-making: Hybrid metrics can provide more information than traditional metrics, which can help businesses make better decisions. For example, a hybrid metric for customer satisfaction can help businesses identify which areas of their customer experience need improvement.
Improve performance: Hybrid metrics can help businesses track their progress over time and identify areas where they can improve. For example, a hybrid metric for customer satisfaction can help businesses track their customer satisfaction scores over time and identify areas where they can improve their customer experience.
Make it easier to compare different entities: Hybrid metrics can make it easier to compare different entities, such as different businesses or different products. For example, a hybrid metric for customer satisfaction can be used to compare the customer satisfaction of different businesses.
.
Hybrid metrics can be used to track a wide range of business objectives, and the specific metrics that are used will vary depending on the specific objectives of the business. However, by combining data from multiple sources, hybrid metrics can provide a more holistic view of performance and help businesses to identify areas for improvement.
And visualizing Hybrid Metric is another topic that helps to share and discuss values from a more holistic point of view.
See here „https://hybrid-metrics.com/„